Background information
ELISA was proposed by Dutch scholars Van Weeman and Schurrs and Swedish researchers Engvall and Perlman in the early 1970s. Initially, it was mainly used for the detection of viruses and bacteria. In the late 1970s, it was widely used for the qualitative and quantitative determination of antigens and antibodies, covering the quantitative detection of hapten molecules such as some drugs, hormones and toxins. Due to its high specificity, strong sensitivity, simple and rapid, does not need expensive equipment, especially suitable for the screening of a large number of samples and other advantages, has become one of the most widely used methods in food safety inspection.
Basic introduction
The basis of ELISA is the solid-phase antigen or antibody and the enzyme-labeled antigen or antibody. First of all, antigen or antibody will bind to the surface of the solid phase carrier somehow, then add the samples, it will form antigen-antibody complexes after reacting with antigen or antibody immobilized on the surface of the solid phase carrier, subsequently combined with compound enzyme labeled antigen or antibody, after joining the substrate color reaction will happen, we can conduct qualitative or quantitative analysis according to color depth. Because of the high catalytic efficiency of enzyme, the reaction effect can be greatly amplified, so that the determination method has a high sensitivity. According to the source of reagents, the situation of samples and the conditions for detection, ELISA techniques mainly include double antibody sandwich method, double antigen sandwich method, indirect method, competition method, capture enveloping method and ABS-ELISA method.
The components of ELISA
Coated Plates: 96 wells plates coated with either inactivated antigen or antibody
Sample diluent: use before adding sample
Controls: positive control---contains Ab/Ag; negative control---without Ab/Ag
Conjugate: enzyme-labeled antibodies or antigens
Substrate: react with enzyme
Wash concentrate: wash away unbound materials from the plates
Stop solution: stops the enzyme-substrate reaction
Main steps
The antigens or antibodies on the surface of the solid phase carrier still maintain the immunological activity, while the enzyme-labeled antigens or antibodies retain both their immunological activity and enzyme activity. Therefore, in the actual detection process, the tested sample (contains the antibody or antigen) reacts with the antigen or antibody on the surface of the solid phase carrier to form an antigen-antibody complex. And through washing, can make the antigen-antibody complexes formed on the solid phase carrier and other unbound substances apart, then add the enzyme labeled antigen or antibody, it also can be bound with the complex fixed on the solid carrier, so the amount of enzyme fixed on the solid phase carrier was positively correlated with the amount of tested compound in the sample, after joining enzyme reaction substrate, enzymatic reactions generated non-ferrous products, the color depth and the amount of tested compound in the sample were positively correlated, so the qualitative or quantitative analysis can be conducted according to the shades of color.

Principle of ELISA
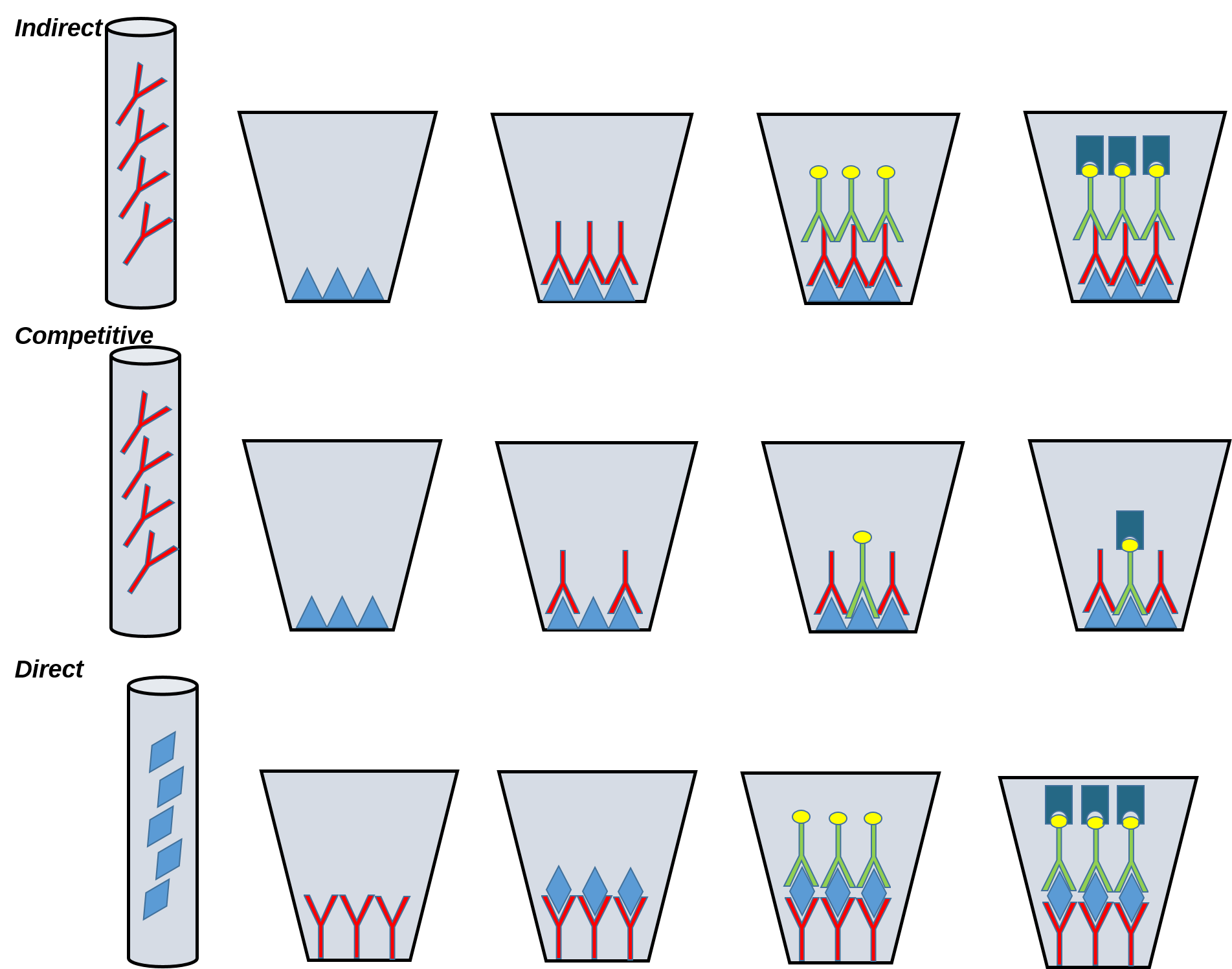
Indirect Format
In the indirect format, the sample antibody is sandwiched between the antigen coated on the plate and an enzyme-labeled, anti-species globulin conjugate. The addition of an enzyme substrate-chromogen reagent causes color to develop. This color is directly proportional to the amount of bound sample antibody. The more antibody presents in the sample, the stronger the color development in the test wells. This format is suitable for determining total antibody level in samples.
Competitive Format
In this format, the specific sample antibodies compete with, or block, the enzyme-labeled, specific antibody in the conjugate. The addition of an enzyme substrate-chromogen reagent causes color to develop. This color is inversely proportional to the amount of bound sample antibody. The more antibodies present in the sample, the less color development in the test wells.
Direct Format
In the antigen-capture format, the antigen in the sample is sandwiched between antibodies coated on the plate and an enzyme-labeled conjugate. The antibody conjugate can be either monoclonal or polyclonal. The addition of an enzyme substrate-chromogen reagent causes color to develop. This color is directly proportional to the amount of the target antigen present in the sample.
Introduction of our products
You can find all our products based on the ELISA in link below.



